Machine Learning-Assisted Manipulation and Readout of Molecular Spin Qubits
Interesting application in
Machine Learning to control Molecular Spin Qubits
by our partner Università degli Studi di Modena e Reggio Emilia
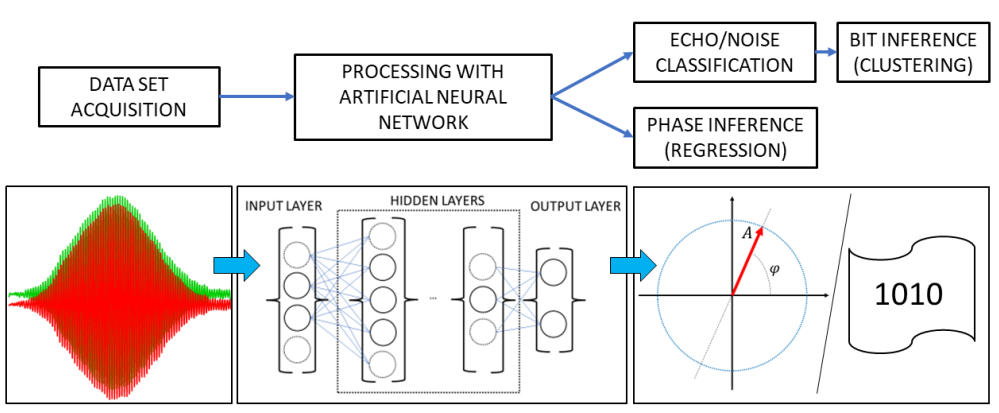
Machine Learning finds application in the quantum control and readout of qubits. In this work we apply Artificial Neural Networks to assist the manipulation and the readout of a prototypical molecular spin qubit – an Oxovanadium(IV) moiety – in two experiments designed to test the amplitude and the phase recognition, respectively. We first successfully use an artificial network to analyze the output of a Storage/Retrieval protocol with four input pulses to recognize the echo positions and, with further post selection on the results, to infer the initial input pulse sequence. We then apply an artificial network to ascertain the phase of the experimentally measured Hahn echo, showing that it is possible to correctly detect its phase and to recognize additional single-pulse phase shifts added during manipulation.
The home-made heterodyne spectrometer used for the generation of MW pulses and time domain acquisition is based on an Arbitrary Waveform Generator by Active Technologies. In this work we exploit the input and output IQ mixers (Marki-IQ-0618LXP double-balanced mixers) to perform two-channels generation of the input pulses and quadrature detection of the output signal, respectively (see Supplementary Information for details). The sample and the resonator are cooled-down to 4 K into a commercial Quantum Design Physical Properties Measurement System (QD
PPMS), which is also used to apply the external static magnetic field.
Our Storage/Retrieval protocol consists of a train of 4 weak MW pulses equally-spaced in time, with duration tp = 40 ns and interpulse delay td = 300 ns. A π pulse with duration tπ = 190 ns is sent after a delay τ = 1200 ns with respect to the last pulse of the input train. A relaxation time trelax = 15 ms is added at the end of the sequence to avoid sample saturation. The refocusing occurs after an additional delay τ with respect to the π pulse, giving a train of weak output echoes. This protocol allows us to use the spin ensemble as a temporary memory for information [51, 68, 69]. In the experiments of this work we exploit the 4 input pulses to codify into the ensemble the binary sequences corresponding to 16 decimal numbers (from 0 to 15, i.e. from 0000 to 1111). An input pulse ON corresponds to the classical logical bit 1 (visible output echo), while a pulse OFF gives the classical logical bit 0 (no output echo). We denote the position of each pulse in the input train with the index i = 1, . . . , 4, according to the order of generation on the AWG. In other words, the index i will give the Storage order into the ensemble and the weight of the bit from the most significant to the least significant one. For each input sequence, the measured raw trace acquired by the oscilloscope results from 4000 averages.
The full paper is available HERE
Ferrara – Italy, 26.08.2022